2025 Deep Learning-Enabled Diagnosis of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Using Pulse Volume Recording Waveforms: An In-Silico Study
본문
- Journal
- Sensors
- Date
- 2025-11
- Citation Index
- SCIE (IF: 3.5, Rank: 23.8%)
- Vol./ Page
- Vol. 25, No. 21 pp. 6678
- Year
- 2025
- Link
- https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/25/21/6678 80회 연결
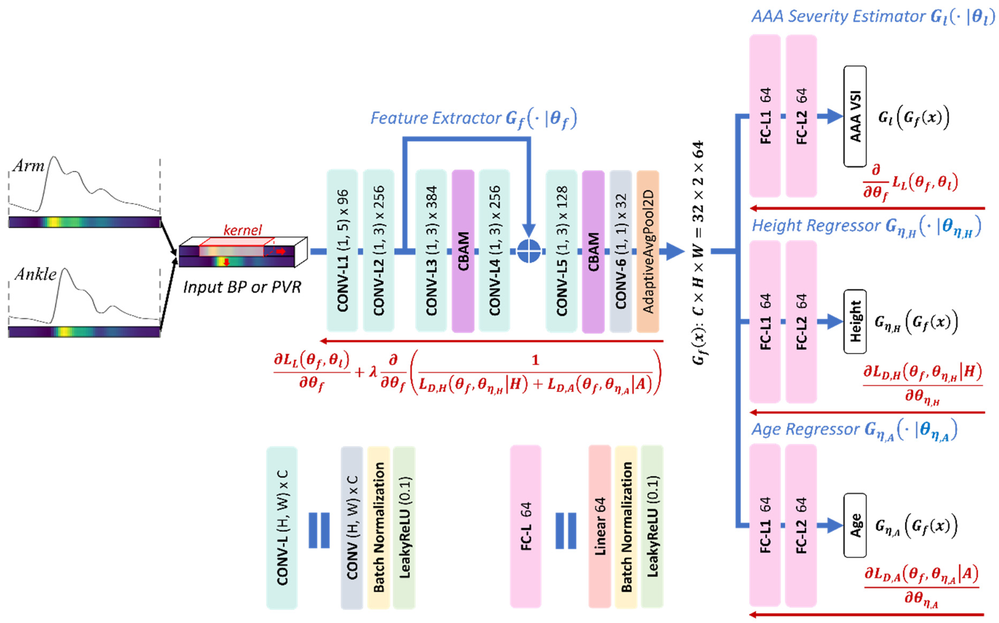
This paper investigates the feasibility of diagnosing abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) via deep learning (DL)-enabled analysis of non-invasive arterial pulse waveform signals. We generated arterial blood pressure (BP) and pulse volume recording (PVR) waveform signals across a diverse synthetic patient cohort using a systemic arterial circulation model coupled with a viscoelastic model relating arterial BP to PVR while simulating a range of AAA severity levels. We confirmed the plausibility of the synthetic data by comparing the alterations in the simulated waveform signals due to AAA against previously reported in vivo findings. Then, we developed a convolutional neural network (CNN) with continuous property-adversarial regularization that can estimate AAA severity from brachial and tibial PVR signals. We evaluated the algorithm’s performance in comparison with an identical CNN trained on invasive arterial BP waveform signals. The DL-enabled PVR-based algorithm achieved robust AAA detection across different severity thresholds with area under the ROC curve values >0.89, and showed reasonable accuracy in severity estimation, though slightly lower than its invasive BP counterpart (MAE: 12.6% vs. 10.3%). These findings suggest that DL-enabled analysis of PVR waveform signals offers a non-invasive and cost-effective approach for AAA diagnosis, potentially enabling accessible screening through operator-agnostic and point-of-care technologies.
