2025 Integrated Optimization of Ply Number, Layer Thickness, and Fiber Angle for Variable-stiffness Composites Using Dynamic Multi-fidelity Surrogate Model
본문
- Journal
- Thin-Walled Structures
- Date
- 2025-01
- Citation Index
- SCIE (IF: 6.6, Rank: 5.6%)
- Vol./ Page
- Vol. 206, pp. 112392
- Year
- 2025
- Link
- https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tws.2024.112392 733회 연결
Abstract
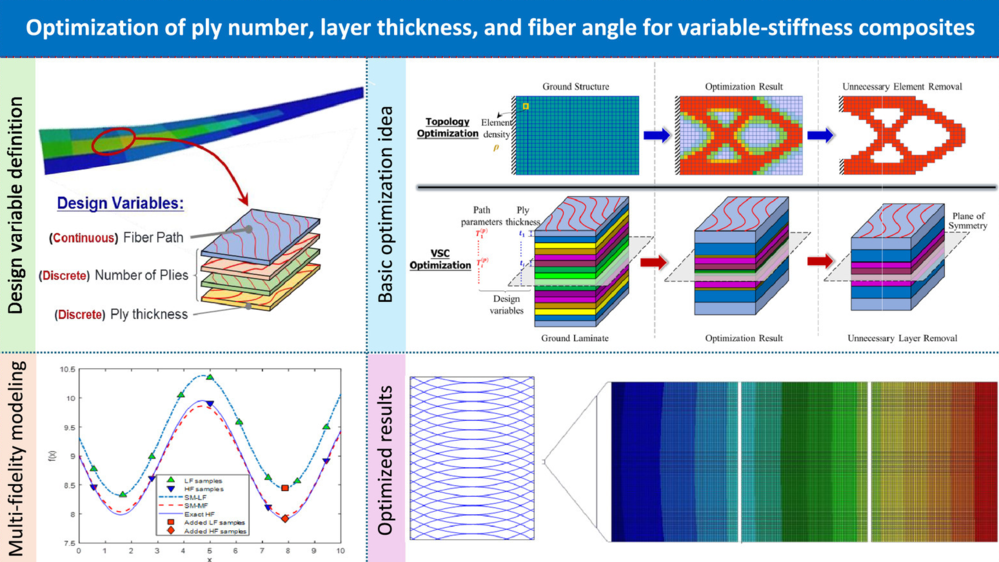
To fully exploit the efficiency of variable-stiffness composite laminates with spatially varied fiber orientation angles, this paper aims at presenting a novel optimization framework for integrated design of ply number, layer thickness, and fiber angle. The optimization problem is innovatively formulated based on the definition of a ground laminate with redundant layers. The basic optimization idea is to seek both unnecessary and necessary layers in this ground laminate. For unnecessary layers, they can be removed and assigned with small-value ply thicknesses, while necessary layers are retained in the ground laminate and corresponding ply thicknesses and fiber angles are optimally determined using discrete and continuous variables, respectively. Since variable-stiffness composite laminates always require high-fidelity analysis models to accurately capture the spatial characteristics of varying fibers, this results in a time-consuming process. To alleviate this problem, a multi-fidelity surrogate model with an exponent-based comprehensive correction is originally proposed based on Gaussian process regression, generating an approximate problem to replace the original one. The genetic algorithm and sequential quadratic programming method are sequentially employed to solve this approximate problem with mixed design variables. The solution from this procedure is dynamically added to the sampling dataset to update the constructed surrogate model. Numerical benchmark problems and cases studies of a composite plate and a solar wing structure are addressed, demonstrating the efficacy of the newly proposed optimization strategy.
- 이전글Special Section on Uncertainty-Aware Diagnostics and Prognostics for Health Monitoring and Risk Management of Engineered Systems 25.01.10
- 다음글Optimized Relative Entropy for Robust Fault Detection in Excavator Traveling Gearboxes via Smeared Envelope Spectrum Analysis of Cyclo-Non-Stationary Signals 25.03.02
