Abstract
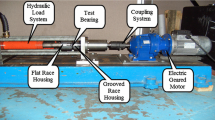
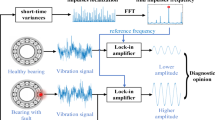
When diagnosing a rolling element bearing (REB), it is important to select the frequency band that has the most defect information. Many band-selection methods have been developed in recent years. Most existing methods target the vibration signal; hence, these methods are often unsuitable for use with acoustic emission (AE) sensors. With existing methods, the large sampling rate and high sensitivity of AE sensor causes huge computing costs and susceptibility to noise. To realize sensitive diagnosis with AE sensors, it is necessary to develop a proper band selection algorithm that operates under noisy conditions and with low computing cost. Thus, this paper proposes a segment-based fault information assisted band selection method for AE sensor data. The proposed method is validated by applying it to both simulated and experimental data. The test data contain random impulsive and non-Gaussian noises to represent the signal from other components and electrical noise from the motor system, respectively. With traditional methods, these noises either interrupt the proper band selection or increase the computing cost; however, the proposed method handles these noises and provides proper band selection with moderate computing cost.


























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Ghamd AM, Mba D (2006) A comparative experimental study on the use of acoustic emission and vibration analysis for bearing defect identification and estimation of defect size. Mech Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2004.10.013
Antoni J (2006) The spectral kurtosis: a useful tool for characterising non-stationary signals. Mech Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2004.09.001
Antoni J (2007) Fast computation of the Kurtogram for the detection of transient faults. Mech Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2005.12.002
Antoni J (2016) The infogram: entropic evidence of the signature of repetitive transients. Mech Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2015.04.034
Antoni J, Borghesani P (2019) A statistical methodology for the design of condition indicators. Mech Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.05.012
Antoni J, Randall RB (2006) The spectral kurtosis: application to the vibratory surveillance and diagnostics of rotating machines. Mech Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2004.09.002
Atamuradov V, Medjaher K, Dersin P, Lamoureux B, Zerhouni N (2017) Prognostics and health management for maintenance practitioners—review, implementation and tools evaluation. Int J Prognos Health Manag. https://doi.org/10.36001/ijphm.2017.v8i3.2667
Barszcz T, Jabłoński A (2011) A novel method for the optimal band selection for vibration signal demodulation and comparison with the Kurtogram. Mech Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2010.05.018
Borghesani P, Pennacchi P, Chatterton S (2014) The relationship between kurtosis- and envelope-based indexes for the diagnostic of rolling element bearings. Mech Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2013.10.007
Caesarendra W, Kosasih B, Tieu AK, Zhu H, Moodie CAS, Zhu Q (2016) Acoustic emission-based condition monitoring methods: review and application for low speed slew bearing. Mech Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2015.10.020
Drouillard T (1996) A history of acoustic emission. J Acoust Emiss 14:1–34
Dwyer RF (1983) Detection of non-Gaussian signals by frequency domain kurtosis estimation. ICASSP IEEE Int Conf Acoust Speech Signal Process Proc. https://doi.org/10.1109/icassp.1983.1172264
Dyer D, Stewart RM (1978) Detection of rolling element bearing damage by statistical vibration analysis. J Mech Des Trans ASME. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3453905
Eftekharnejad B, Carrasco MR, Charnley B, Mba D (2011) The application of spectral kurtosis on acoustic emission and vibrations from a defective bearing. Mech Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2010.06.010
Elforjani M, Mba D (2008) Monitoring the onset and propagation of natural degradation process in a slow speed rolling element bearing with acoustic emission. J Vib Acoust Trans ASME. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2948413
Ferrando Chacon JL, Kappatos V, Balachandran W, Gan TH (2015) A novel approach for incipient defect detection in rolling bearings using acoustic emission technique. Appl Acoust. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apacoust.2014.09.002
Gholizadeh S, Lemana Z, Baharudinb BTHT (2015) A review of the application of acoustic emission technique in engineering. Struct Eng Mech. https://doi.org/10.12989/sem.2015.54.6.1075
Harris TA, Kotzalas MN (2006) Essential concepts of bearing technology. In: Essential concepts of bearing technology. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420006599
He Y, Zhang X, Friswell MI (2009) Defect diagnosis for rolling element bearings using acoustic emission. J Vib Acoust Trans ASME. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4000480
Hu C, Youn BD, Wang P, Taek Yoon J (2012) Ensemble of data-driven prognostic algorithms for robust prediction of remaining useful life. Reliab Eng Syst Saf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2012.03.008
Islam MMM, Kim JM (2017) Time–frequency envelope analysis-based sub-band selection and probabilistic support vector machines for multi-fault diagnosis of low-speed bearings. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-017-0585-2
Kim T, Lee G, Youn BD (2019) PHM experimental design for effective state separation using Jensen-Shannon divergence. Reliab Eng Syst Saf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2019.106503
Kim SJ, Kim K, Hwang T, Park J, Jeong H, Kim T, Youn BD (2022) Motor-current-based electromagnetic interference de-noising method for rolling element bearing diagnosis using acoustic emission sensors. Meas J Int Meas Confeder. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2022.110912
Mauricio A, Qi J, Smith WA, Sarazin M, Randall RB, Janssens K, Gryllias K (2020) Bearing diagnostics under strong electromagnetic interference based on Integrated Spectral Coherence. Mech Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2020.106673
McDonald GL, Zhao Q (2017) Multipoint optimal minimum entropy deconvolution and convolution fix: application to vibration fault detection. Mech Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2016.05.036
Moshrefzadeh A, Fasana A (2018) The Autogram: an effective approach for selecting the optimal demodulation band in rolling element bearings diagnosis. Mech Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.12.009
Nguyen P, Kang M, Kim JM, Ahn BH, Ha JM, Choi BK (2015) Robust condition monitoring of rolling element bearings using de-noising and envelope analysis with signal decomposition techniques. Expert Syst Appl. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2015.07.064
Nguyen HN, Kim J, Kim JM (2018) Optimal sub-band analysis based on the envelope power spectrum for effective fault detection in bearing under variable, low speeds. Sensors (switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051389
Oppenheim AV, Schafer RW (1998) Discrete time signal processing, 2nd edn. Book, New York
Ottonello C, Pagnan S (1994) Modified frequency domain kurtosis for signal processing. Electron Lett. https://doi.org/10.1049/el:19940777
Prabhu KMM (2018) Window functions and their applications in signal processing. In: Window functions and their applications in signal processing. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781315216386
Quezada D, Molina Vicuña C (2015) Damage assessment of rolling element bearing using cyclostationary processing of AE signals with electromagnetic interference. Appl Cond Monit. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-16330-7_3
Randall RB, Antoni J (2011) Rolling element bearing diagnostics—a tutorial. Mech Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2010.07.017
Sikorska JZ, Mba D (2006) Ae condition monitoring: challenges and opportunities. In: Proceedings of the 1st world congress on engineering asset management, WCEAM 2006. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-84628-814-2_14
Smith WA, Borghesani P, Ni Q, Wang K, Peng Z (2019) Optimal demodulation-band selection for envelope-based diagnostics: a comparative study of traditional and novel tools. Mech Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.106303
Smith WA, Randall RB, du Mée X, de C, Peng P (2017) Use of cyclostationary properties to diagnose planet bearing faults in variable speed conditions. In: 10th DST group international conference on health and usage monitoring systems, 17th Australian Aerospace Congress
Sun J (2012) Pulse-width modulation. Adv Ind Control. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4471-2885-4_2
Tan ACC, Kim YH, Kosse V (2008) Condition monitoring of low-speed bearings—a review. Aust J Mech Eng. https://doi.org/10.1080/14484846.2008.11464558
Tandon N, Choudhury A (1999) Review of vibration and acoustic measurement methods for the detection of defects in rolling element bearings. Tribol Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-679X(99)00077-8
Vicuña CM, Höweler C (2017) A method for reduction of Acoustic Emission (AE) data with application in machine failure detection and diagnosis. Mech Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.04.040
Wang P, Youn BD, Hu C (2012) A generic probabilistic framework for structural health prognostics and uncertainty management. Mech Syst Signal Process. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2011.10.019
Westfall PH (2014) Kurtosis as peakedness, 1905–2014. R.I.P. American Statistician. https://doi.org/10.1080/00031305.2014.917055
Youn BD, Hu C, Wang P (2011) Resilience-driven system design of complex engineered systems. J Mech Des Trans ASME. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4004981
Yu K, Lin TR, Tan J, Ma H (2019) An adaptive sensitive frequency band selection method for empirical wavelet transform and its application in bearing fault diagnosis. Meas J Int Meas Confeder. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.10.086
Zhang X, Kang J, Xiao L, Zhao J, Teng H (2015) A new improved Kurtogram and its application to bearing fault diagnosis. Shock Vib. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/385412
Žvokelj M, Zupan S, Prebil I (2016) EEMD-based multiscale ICA method for slewing bearing fault detection and diagnosis. J Sound Vib. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2016.01.046
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Korea Government (MSIT) (Nos. 2021R1A4A2001824 and 2021R1F1A1064460).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
As the first author, S. J. Kim wrote the manuscript and analyzed the data. B. D. Youn and T. Kim supervised the research. They are responsible for this paper as co-corresponding authors. S. Kim and S. Lee assisted in the experiment and data gathering
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Zhen Hu
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Topical Collection: Advanced Optimization Enabling Digital Twin Technology.
Guest Editors: Chao Hu, Vicente A. González, Taejin Kim, Omer San, Zhen Hu.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.J., Kim, S., Lee, S. et al. Effective band-selection algorithm for rolling element bearing diagnosis using AE sensor data under noisy conditions. Struct Multidisc Optim 65, 275 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-022-03360-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-022-03360-4